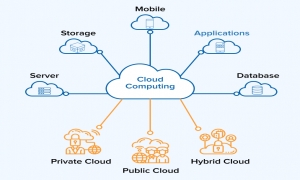
The private cloud environment promises a high level of control and security: in contrast to public clouds, private clouds cannot be accessed by the general public through the Internet. These are operated exclusively for individual organizations such as companies or authorities. Depending on its characteristics, it can be hosted on its own computer or on a server from an external provider. Access to cloud services is done either through a limited intranet or through a closed virtual private network (VPN).
Thus, a private cloud is an internal cloud associated with an organization that makes the application available only to authorized users. Access protection can be done for example by a firewall. Another name for private cloud is company cloud or corporate cloud. Private cloud acts as an organization's internal service provider to users. Like public clouds, private clouds depend on virtualization and distributed computing.
Because this form of cloud computing doesn't have to be shared with other users, it offers a high level of security, control and flexibility. Applications can be upgraded to the individual needs of the organization and can be used very efficiently. The capacity of computers, storage, and networks is tailored to their own needs and is not subject to public cloud constraints. allows rapid adaptation of computer services and billing that depends on the user of the service being used. Especially for organizations that must adhere to strict data security and data processing standards or are subject to state regulations, private cloud is the ideal solution. Thanks to a special architecture of cloud services, the potential for large savings can be achieved compared to conventional IT infrastructure. In some areas, private clouds are used in conjunction with public clouds in the form of what is called a hybrid cloud. It combines the advantages of both worlds into a separate cloud model.
Virtualization as the basis of a private cloud
The technical base of private cloud is virtualization. Using advanced virtualization technology, IT services and resources can be separated from physical devices. The application no longer runs locally at the endpoint or server, but is virtually placed in a cloud environment. Virtualization offers the advantage that resources can be allocated flexibly for various applications. In addition, this increases availability, because the failure of each computer can usually be intercepted by a virtualized environment.
Users can access applications through internal networks or secure the structure of public networks (keywords: VPN). For this purpose, each user receives the rights required by him. He must authenticate himself to cloud services. Compared to traditional IT infrastructure, cloud eliminates the need to run separate servers for individual applications. The virtualized server environment is available for all services.
The four types
Private clouds can be subdivided into four different subtypes. These types are:
- Internal: The company operates its own IT infrastructure for its cloud services.
- Managed : The cloud IT infrastructure is hosted internally but is managed by an outside vendor. Thus, companies can use flexibility and customization of private clouds, whose functions are optimally designed by providers to customers. Thus, its efficiency increases, and the company always has reliable links for all topics related to the cloud.
- Hosted: Hosted private clouds are in the cloud service provider's external data center. This provider manages the cloud on behalf of their respective companies and provides applications that are suitable for users.
- Private Cloud Community: Private Cloud Community is a special form of private cloud. Here, several companies can access a shared private cloud. Companies usually come from the same industry or are part of a group. Therefore, the private cloud community is also referred to as an industry-specific private cloud.
In internal private clouds, companies or organizations themselves run IT infrastructure for their services. Even with private cloud infrastructure that is managed for the cloud, it is hosted internally, but is managed by an external provider, maintained and monitored. Hosted private cloud is in the cloud service provider's external data center. It runs a cloud on behalf of organizations that are separate from other environments and makes applications available only to organizational users. Community Private Cloud is a special form of private cloud where several companies, for example from the same industry or from expanded group networks, access the same cloud. This is almost an industry-specific private cloud.
Private cloud advantage
Private cloud users benefit from the many advantages of cloud computing without having to give up control of their data and IT infrastructure to external providers. Compared to conventional structures, complete IT can be made more streamlined and operate more efficiently and cost-effectively. With certain hardware virtualization and decoupling, the server environment is consolidated.
Resources are bundled in a central group and at the same time flexible. Capacity on demand and can be measured in the near future. Compared to public cloud, private cloud offers further benefits. Users have exclusive access to cloud performance and bandwidth. Limitations because simultaneous use of third parties is not expected. Protected and isolated private cloud operations minimize security risks for the organization. If special security measures must be taken, this is possible in a simple and specific application. The interests of third parties are not considered.
Differentiation of internal personal cloud to public cloud and security aspects
As far as the basic technical public and private cloud are concerned, there is no difference. However, private clouds are not public and are operated and managed separately. Only authorized users have access to applications and data. The organization maintains full control over its data at all times. Due to specific data protection requirements, public cloud use can be prohibited.
Internal private cloud is clearly distinguished from the cloud structure offered, for example, by Amazon or Microsoft. In public cloud, customers need to share virtual infrastructure. In addition, in many cases it is not possible to determine where data is hosted.
The features and advantages :
- Higher levels of privacy and security. This model implements a higher level of security, such as using a different pool technique from resources with limited access to connections that are only made from corporate firewalls, using special lines, to ensure that operations are not out of reach.
- Better control. Can only be accessed by one organization, and the organization will have the ability to configure and manage their servers according to their needs to achieve a customized network solution.
- Cost and energy efficiency. By implementing this cloud model organizations can increase the allocation of resources within their organization by ensuring that the availability of resources for certain business functions or departments can directly and flexibly respond to their requests. Although not as effective as the costs of Public Cloud services because of the smaller economies of scale and increased management costs, makes more efficient use of computing resources from traditional LANs, because they minimize investment into unused capacity. This not only can provide cost savings but also can reduce the carbon footprint of the company.
- Improve reliability. Even though resources (servers, networks etc.) are hosted internally, the creation of a virtualization environment means that the network is more resistant to individual failures in all physical infrastructure. Virtual partitions can, for example, extract their resources from available servers. In addition, where cloud is hosted on third-party providers, organizations can still have the advantage of the physical security provided for hosted infrastructure in the data center.
- Cloud bursting. Some providers may offer the opportunity to employ cloud bursting, in the Private Cloud offering, when there is a surge in demand. This service allows providers to switch functions that are not sensitive to the Public Cloud to free up more space in the Private Cloud for sensitive functions .
Deficiency
- Restricted Operation Area. only locally accessible and very difficult to implement globally.
- Expensive Implementation. Buying new hardware and software to meet demand is relatively too expensive, because you have to prepare hardware and software in each organization
- Limited Scalability. can only be scaled in internal host resource capacity
- Requires a Cloud Expert. To manage it, an organization must prepare 1 person who has skills in the field of cloud, to do data maintenance and user access to using the private cloud.
Private cloud economy
One of the biggest misconceptions about personal cloud is that the cloud will save money. It can and often does, but basically not.
Upfront costs can be very large. For example, automation technology, an important part of personal cloud networks, can be a significant investment for many IT organizations. The result can be the ability to reallocate resources more efficiently, and allow several organizations to reduce overall capital expenditure for new hardware, which can also save money. But overall savings are not guaranteed.
Gartner analysts say the main benefits of driving to adopt a private cloud model should not be cost savings, but rather increase dynamic agility and scalability, which can increase time-to-market for businesses that utilize technology.
Private clouds can be in the public cloud
Many people associate a private cloud with those in the private data center and public cloud organizations as coming from third-party service providers. But as noted by NIST, while private clouds can be owned, managed and operated by private organizations, the infrastructure may be located outside the location.
Many providers sell private cloud outside the location, which means that while physical resources are located in third-party facilities, they are dedicated to one customer. They are not shared, because they are in the public cloud, with a collection of multi-tenant resources among many customers. Personal cloud computing is determined by privacy, not location, ownership, or management responsibility.
When dealing with cloud providers, be careful with the definition of security. Some vendors may, for example, outsource their data center operations to collocation facilities where they may not dedicate hardware to each customer. Or they can pool resources among customers but say they guarantee privacy by separating them using VPN. Investigate the details of private cloud offers outside the location, Bittman advises.
Private cloud is more than IaaS
Infrastructure as a service is a big reason for adopting private cloud architecture, but that does not mean only its usefulness. Software and platforms as services are also important, although Bittman said IaaS is the fastest growing segment.
"IaaS only provides the lowest level data center resources in a way that is easy to consume, and does not fundamentally change the way IT is done," he said. Platform as a service (PaaS) is where organizations can create special applications built to run on cloud infrastructure. PaaS is present in a public or personal sense as well, having application development services that are held either in the data center on the premises or in a specific environment of the provider.
Personal cloud is not always private
Private cloud is the natural first step towards cloud networks for many organizations. This provides access to the benefits of the cloud - dexterity, scalability, efficiency - without some security issues, perceived or real, that come using public cloud. But Bittman estimates that as the cloud market continues to grow, organizations will be open to the idea of using public cloud resources. Service level agreements and safety precautions will be ripe and the effects of outages and downtime will be minimized.
Finally, Gartner predicts, the majority of private cloud deployments will become hybrid clouds, which means they will utilize public cloud resources. That means your personal cloud today, maybe a hybrid cloud tomorrow. "By starting with a private cloud, IT positions itself as an intermediary for all services for companies, whether private, public, hybrid or traditional. Private people who evolve into hybrids or even the public can retain ownership of self-service, and, therefore, customers and interface.This is part of the vision for the future of IT that we call 'hybrid IT.' "