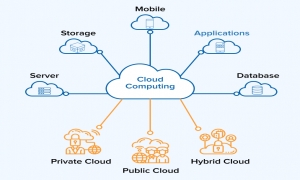
If you have a choice between a hybrid cloud and a private cloud, you have to consider a lot about its most important differences and advantages.
Hybrid clouds are something that is very important for IT companies and business leaders. Hybrid cloud seeks to balance between control and self-service capabilities of personal cloud and scalability and comprehensive service options from public cloud. The resulting hybrid cloud can empower companies to send and migrate applications under compromise carefully considered in terms of security, compliance, resilience, performance, scalability, and cost effectiveness.
However, hybrid cloud can also be uncomfortable in terms of investment and efficient orchestration. Before choosing between hybrid cloud and private cloud, you must be familiar with some of the problems and problems associated with this cloud technology.
Advantages and limitations of private cloud
A private cloud is a cloud deployment that is bought and operated by the company itself. All personal resources and cloud services only serve exclusive companies.
A private cloud can be for example in a data center on a site to deploy. This will make the company responsible for buying, installing, configuring and maintaining all the hardware and software infrastructure needed to support the cloud and its users.
Private clouds can also be hosted by external service providers. In this case, service providers are responsible for infrastructure while companies get exclusive access to the resources needed through secure private networks (such as Virtual Private Networks, VPN).
Private cloud can bring significant effort and investment. However, they are often chosen by companies that want to take advantage of cloud computing (such as flexibility, self-service for users, or automation) while still maintaining complete control of the computing environment. Clients sampling with these needs are government entities or financial institutions.
Private cloud offers important benefits but is also subject to limitations. Companies are charged for personal cloud infrastructure (either directly through a field installation or indirectly through payment to a hosting provider). Ultimately, this means that the amount of infrastructure and resources is inevitably limited.
In addition, the costs, expertise, and software companies needed to use cloud services are usually limited to the private cloud. For example, private cloud requires a complex stack of software, such as OpenStack or Apache CloudStack. Deploying existing virtualization platforms, this stack provides self-service, automation, ticketing, instance storage and management, load balancing, scalability, and other features and services that businesses need for a functioning cloud.
But implementing, securing, and maintaining complex stacks, services, and supporting middleware (such as databases) requires people with proven expertise in the choice stack. This can result in additional requirements for IT personnel rather than reduction.
The prospect of greater investment in infrastructure and personnel has an inhibiting effect on the willingness to operate a private cloud on the spot and in place. By comparison, the public cloud offers a far more scalable infrastructure, a richer set of cloud services, and a pay-as-you-go billing model that can't be matched by a private cloud.
Cloud Hybrid or Private Cloud: Take the best of both worlds
Companies that need direct security and control over the private cloud, but at the same time long for scalability and versatile services from the public cloud, can find solutions with the adoption of a hybrid cloud. In this way, companies can mix local private cloud or hosted with available public cloud, such as AWS, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, or others. With professional implementation, the hybrid cloud provides a single and integrated platform to easily use resources, services, and workloads in two different clouds.
For example, consider workloads that require more security and monitoring in the private cloud, while placing developer testing or workload of developers or everyday web servers into the public cloud. In addition, administrators can migrate workloads and data between the two clouds.
Workloads in private clouds can be migrated to public clouds, where there is greater scalability and the cost of processing workloads may be lower. Another reason for transferring workloads may be temporary network traffic jams or other relevant events in the company environment. This workload can also be transferred back to the private cloud if circumstances change over time. In fact, cloud hybrid vs. Personal Cloud is the best choice and a dynamic deployment environment for each workload.
However, the road to the hybrid cloud is full of traps. For example, public cloud and private cloud need to communicate locally. Usually private cloud must use API from public cloud. And this can creep in the first dependence on one provider. It's possible to design a private cloud that can interact with more than one public cloud. However, this leads to a drastic increase in the complexity of private clouds and thus also produces a hybrid cloud.
As another example, it should be noted that hybrid cloud must be equipped with the right management tools. Ideally, one tool must be selected and implemented. This ensures shared visibility and control capabilities through private cloud and public cloud. Such a step can be a deviation from a familiar tool. This can mean a new learning curve. And that might require the development of new policies and practices that avoid mistakes, maintain security, and help keep public cloud costs under control.
Private Cloud refers to cloud solutions that are dedicated to use by one organization.
Private cloud benefits for business organizations include:
- Special and safe environment that cannot be accessed by other organizations.
- Compliance with strict regulations because organizations can run protocols, configurations, and steps to adjust security based on unique workload requirements.
- Scalability and high efficiency to meet demands that cannot be predicted without compromising security and performance.
- High SLA performance and efficiency.
- Flexibility to change infrastructure based on the ever-changing business and IT needs of the organization.
Limitations:
- Expensive solutions with relatively high total cost of ownership compared to public cloud alternatives for short-term use cases.
- Cellular users may have limited access to the private cloud taking into account the high security measures that exist.
- Infrastructure may not offer high scalability to meet unexpected demand if the cloud data center is limited to computing resources in place.
Hybrid Cloud refers to a cloud infrastructure environment that is a mixture of public and private cloud solutions.
Hybrid Cloud advantages for business organizations include:
- Spread is driven by a flexible policy to distribute workload in public and private infrastructure environments based on security, performance and cost requirements.
- Scalability of the public cloud environment is achieved without exposing IT workloads that are sensitive to inherent security risks.
- High reliability because services are distributed in various data centers throughout public and private data centers.
- Improve the security posture because sensitive IT workloads run on special resources in the private cloud while regular workloads are spread in inexpensive public cloud infrastructure to be exchanged for investment costs.
Limitations:
- That can be expensive.
- Strong compatibility and integration is needed between cloud infrastructure that covers various locations and categories. This is a limit to the spread of public clouds, where organizations do not have direct control over infrastructure.
- The complexity of additional infrastructure was introduced when the organization operated and managed a growing mix of public and private cloud architectures.
The choice between a private cloud solution, and hybrid depends on various factors, use cases, and limitations. In the real world, this is not a wrong / or wrong situation, especially because organizations tend to use all three types of cloud solutions by considering the value propositions and the value of the inherent value.